O argumento de um designer inteligente necessário para configurar as redes metabólicas para a origem da vida.
http://elohim.heavenforum.org/t256-o-argumento-de-um-designer-inteligente-necessario-para-configurar-as-redes-metabolicas-para-a-origem-da-vida
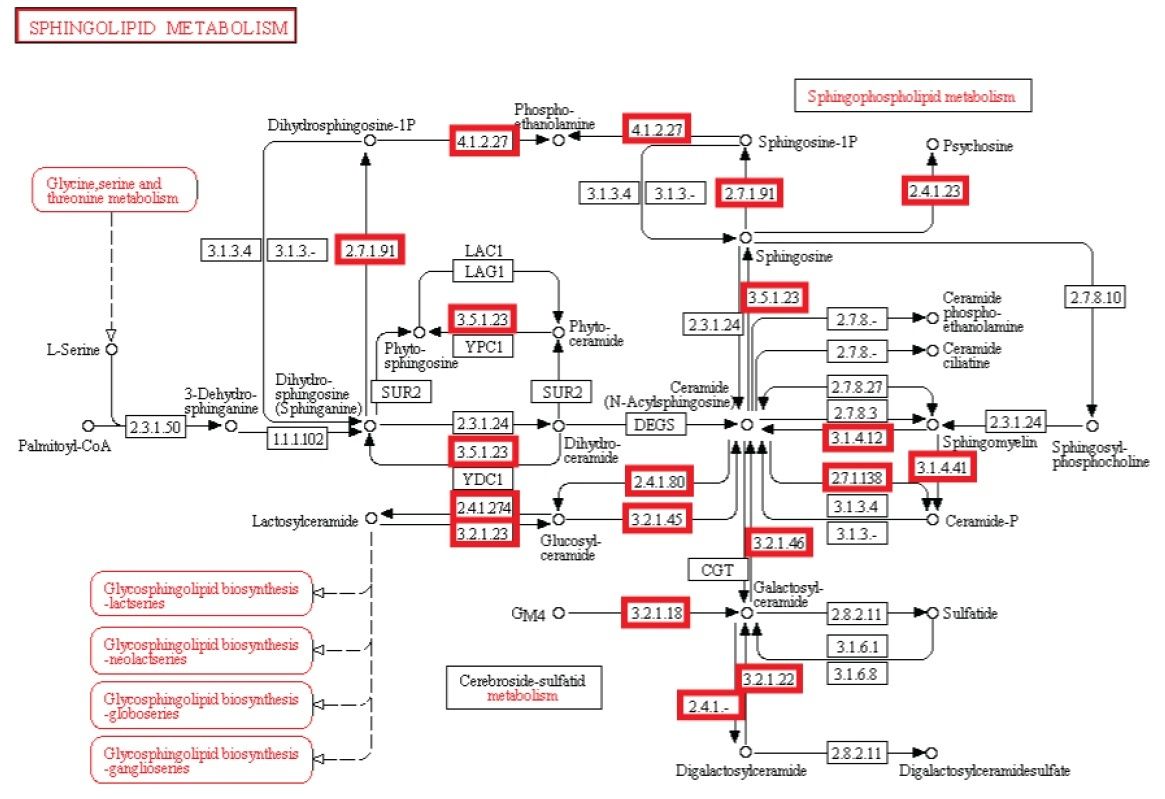
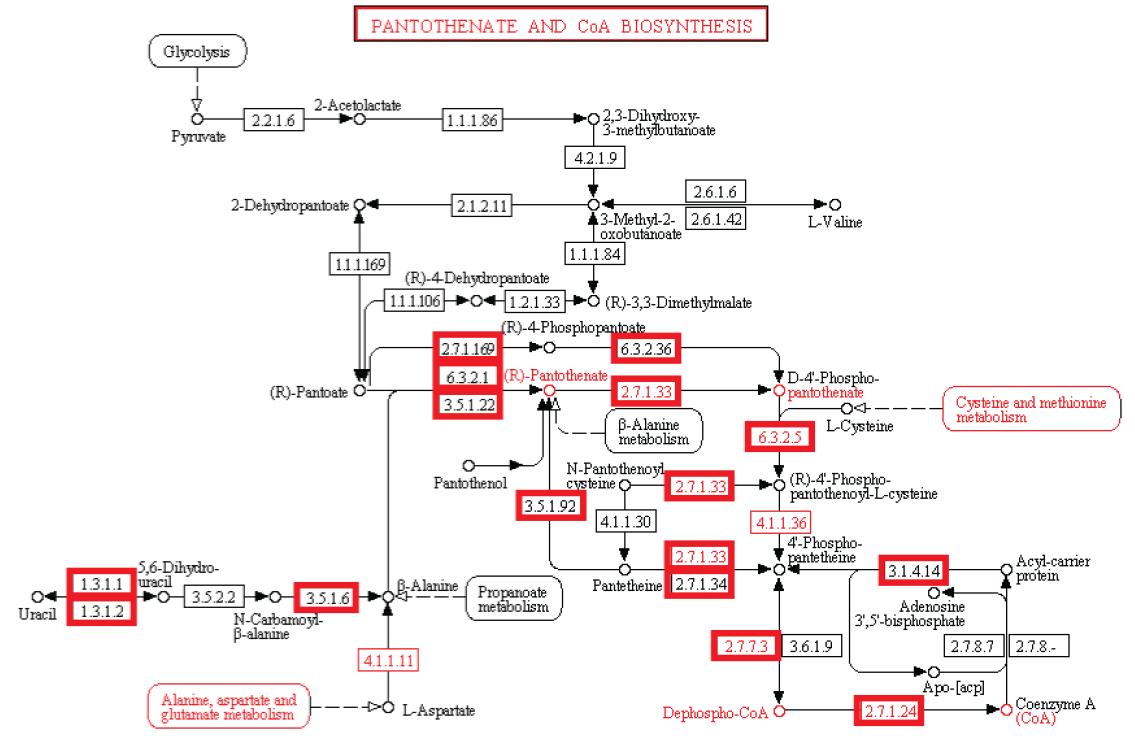
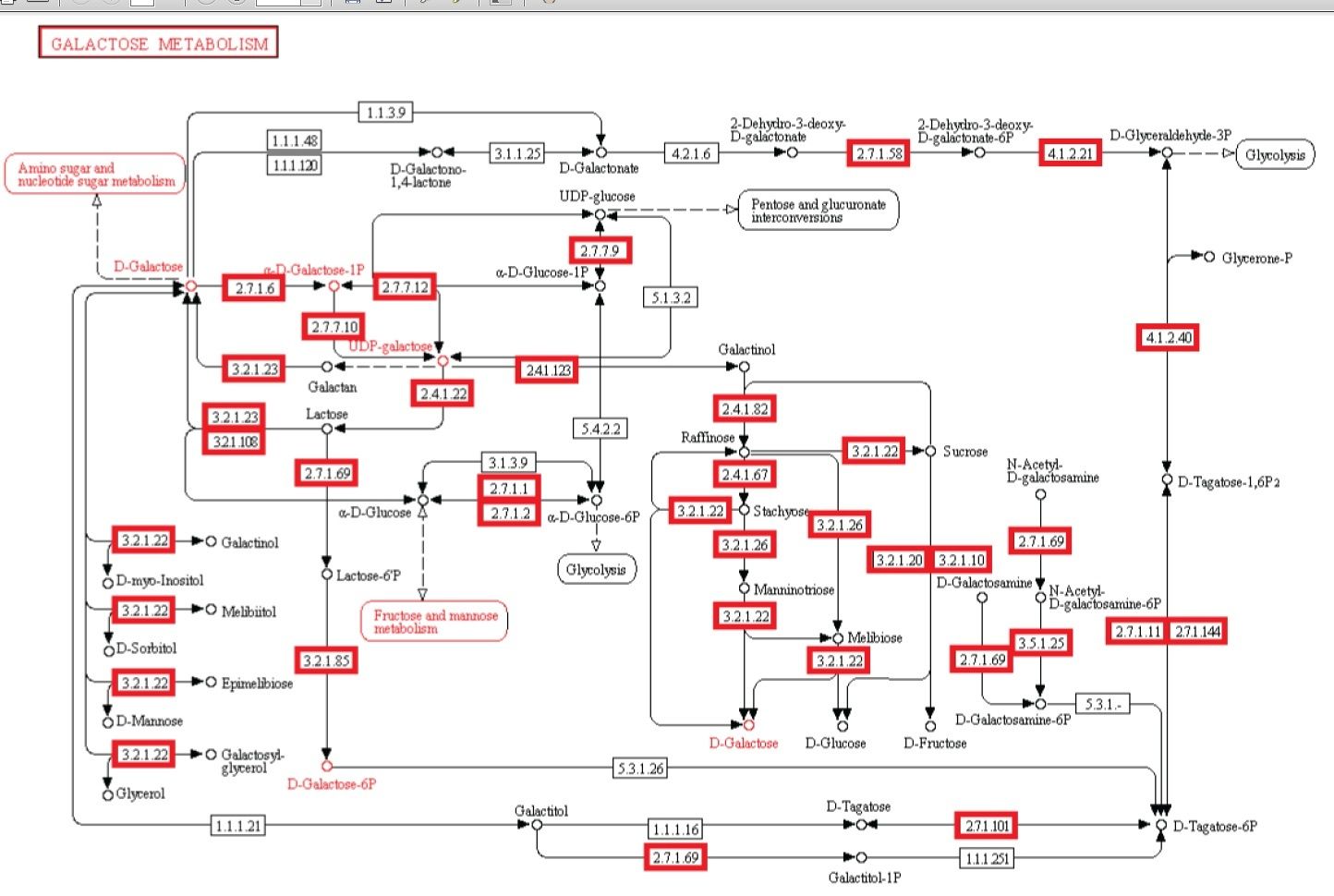
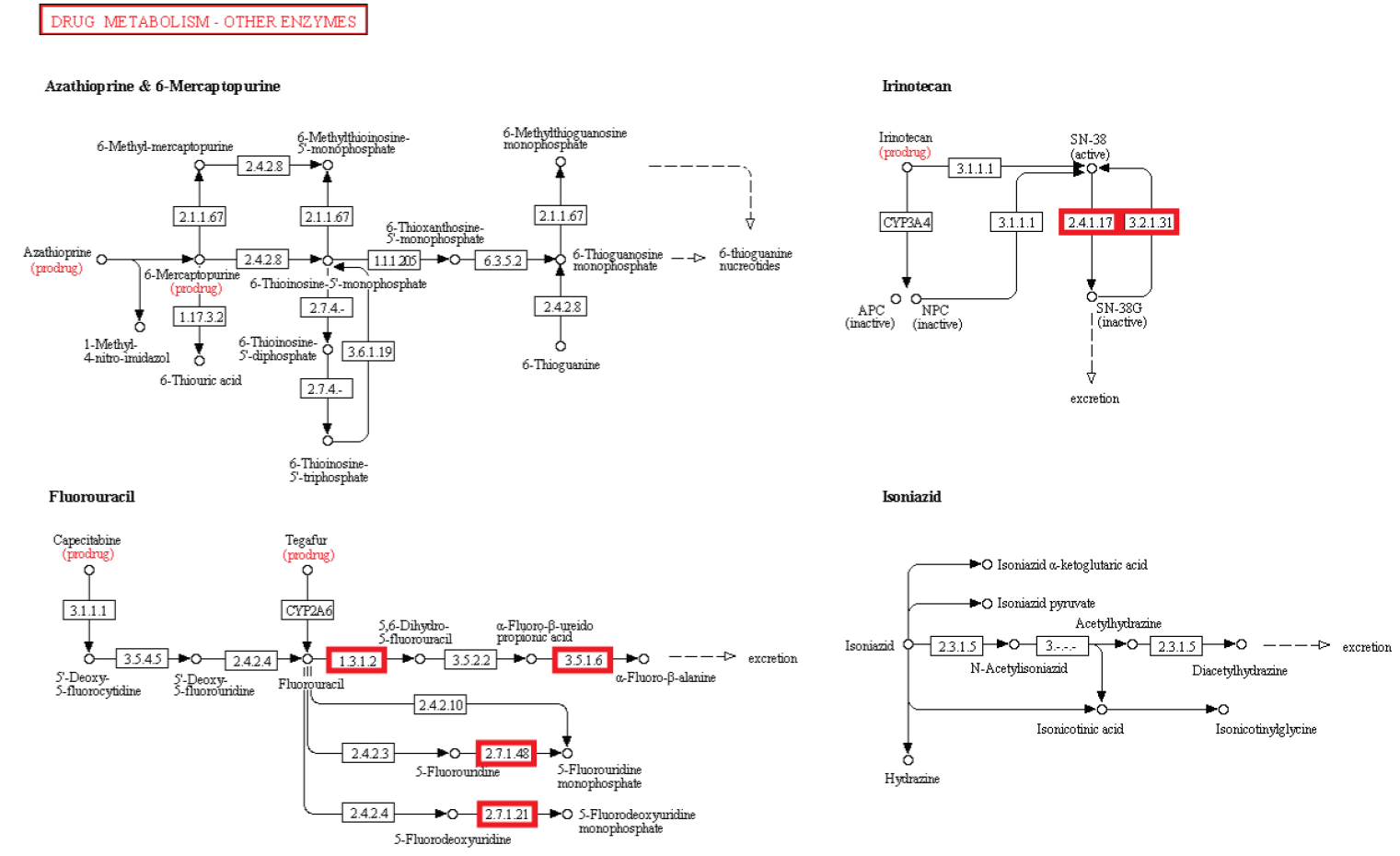
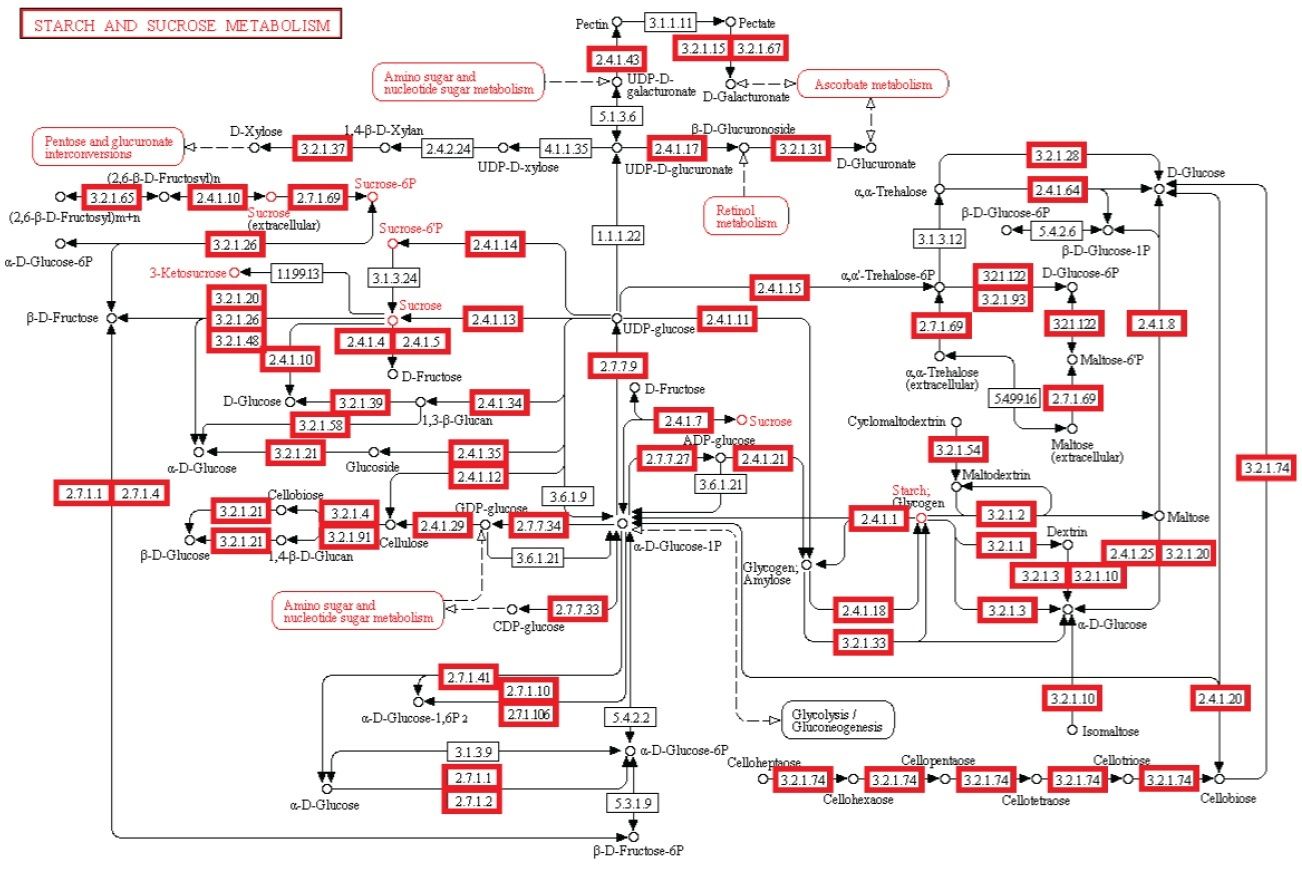
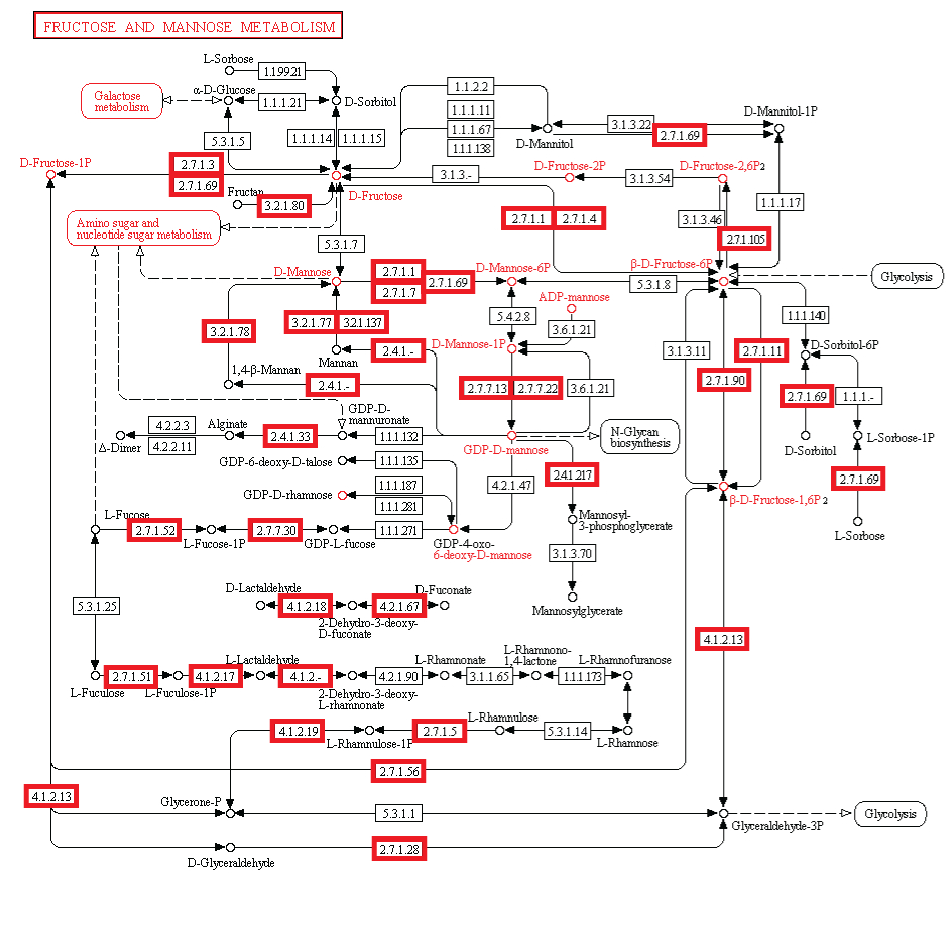
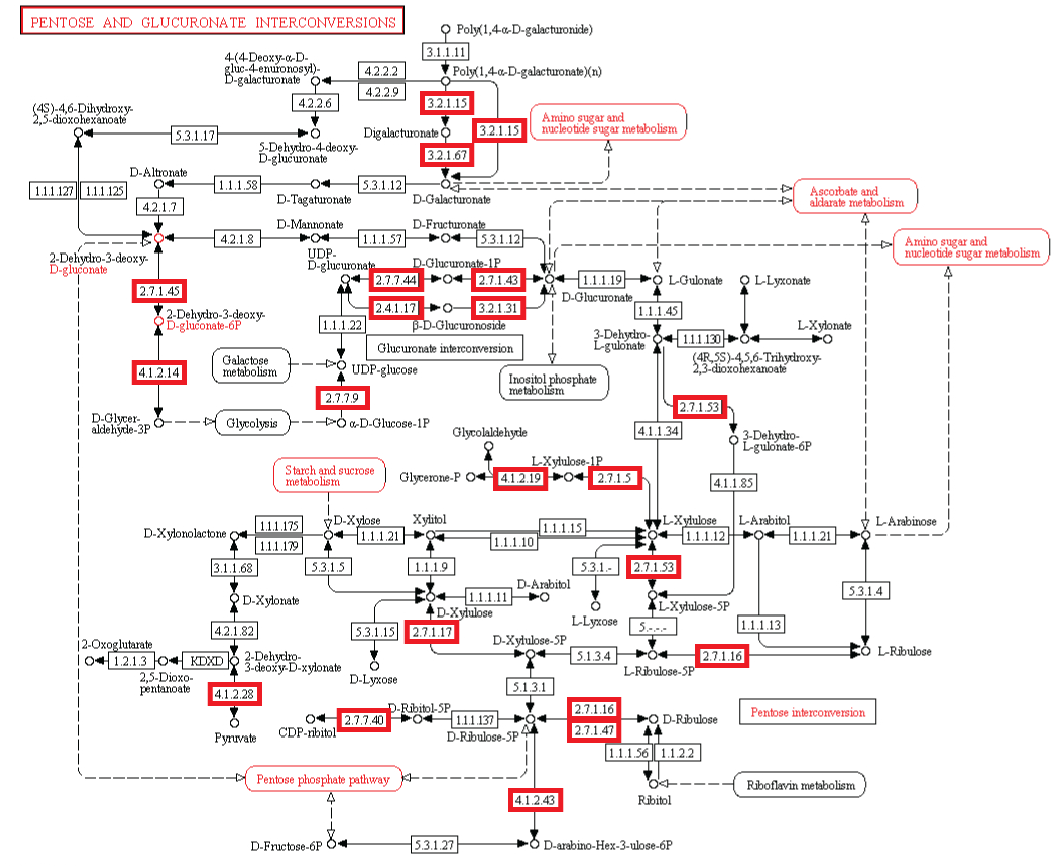
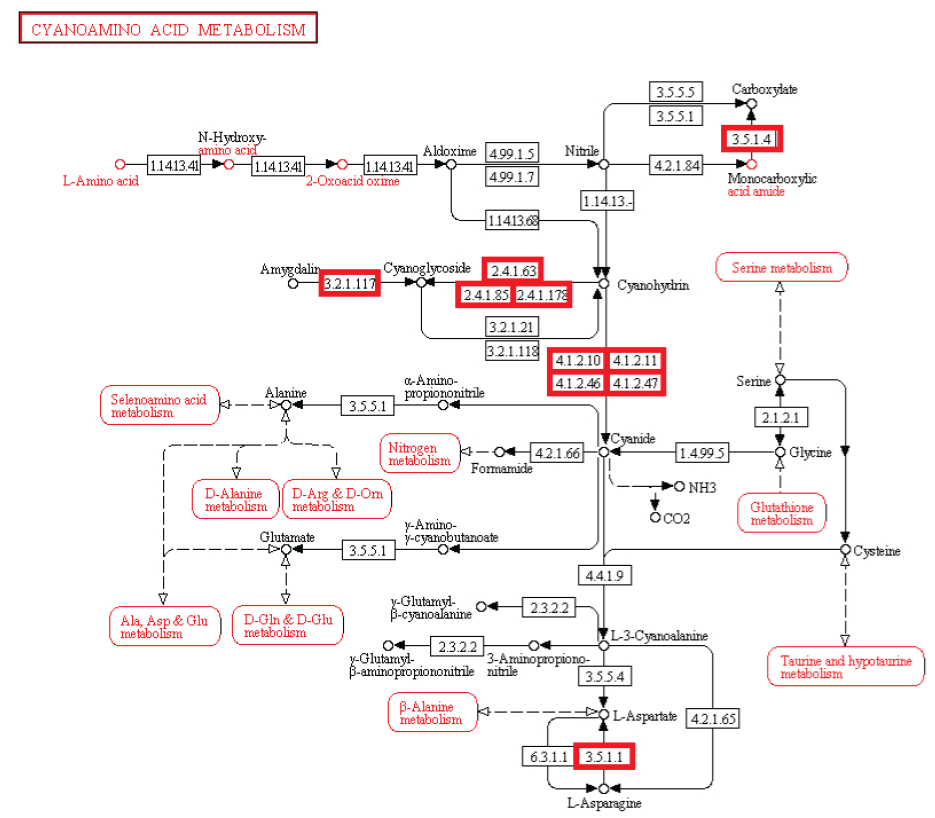
Observação: A existência de vias metabólicas é crucial para a função molecular e celular. Apesar do fato que genomas bacterianos diferem substancialmente em seus tamanhos e repertórios de genes, não importa quão pequenos, devem conter todas as informações para permitir que a célula possa executar muitas funções essenciais que dão a célula a capacidade de manter a homeostase metabólica, reproduzir e evoluir , as três principais propriedades de células vivas. (Gil et al. 2004) De fato, o metabolismo é um dos processos celulares mais conservadas. Ao integrar dados de genômica comparativa e estudos de eliminação de grande escala, o estudo científico de "análises estruturais de um metabolismo mínimo hipotético" propõe um conjunto de genes mínimo compreendendo 206 genes codificadores de proteínas de uma célula mínima hipotética. O documento lista 50 enzimas / proteínas necessárias para criar uma rede metabólica implementada por um genoma mínimo hipotético para a célula mínima hipotética. Os 50 enzimas / proteínas, e da rede metabólica, devem ser totalmente implementados para permitir uma célula para manter suas funções básicas.
Hipótese (Previsão): A origem de vias metabólicas irredutíveis biológicos que também necessitam de regulamentação e e que são estruturadas como uma cascata,
semelhante a placas de circuitos electrónicos, são melhor explicadas pela ação criadora de um agente inteligente.
Experiência: investigações experimentais de redes metabólicas indicam que elas estão cheias de nós com enzimas / proteínas, que requerem para a sua informação de síntese códigos ricos baseados na linguagem, armazenados em DNA. As estruturas hierárquicas têm provado ser mais adequadas para capturar a maior parte das características das redes metabólicas (Ravasz et ai, 2002). Verificou-se que os metabolitos só podem ser sintetizados, se carbono, nitrogênio, fósforo e enxofre e os blocos de construção básicos gerados a partir deles no metabolismo central são disponíveis. Isto implica que as redes reguladoras engrenagem atividades metabólicas para a disponibilidade desses recursos básicos. Então, um circuito metabólico depende do produto de outros produtos, proveniente de outras vias metabólicas, centrais, dependendo um do outro, como em um Cascata. Mais notável é que loops de feedback foram encontrados serem necessários para regular o fluxo metabólico, e as atividades de muitas ou de todas as enzimas em uma via. Em muitos casos, as vias metabólicas são altamente ramificadas, em cujo caso é muitas vezes necessário fazer modificações de fluxos através de parte da rede, enquanto deixando-os inalterados ou reduzi-los em outras partes da rede (Curien et al., 2009). Estes são interligados de uma forma funcional, resultando em uma célula viva. As redes metabólicas biológicas são perfeitamente integradas, de modo que as alterações significativas inevitavelmente danificam ou destroem a função. Mudanças no fluxo muitas vezes exigem mudanças nas atividades de várias enzimas em uma sequência metabólica. Síntese de um metabolito tipicamente requer a operação de muitos caminhos.
Conclusão: Independentemente da sua complexidade inicial, a vida metabólica com base química de auto-sustentação não poderia ter surgida na ausência de um mecanismo de replicação genético assegurando a manutenção, estabilidade e diversificação dos seus componentes. Na ausência de quaisquer mecanismos hereditários, as cadeias de reação autotrófitos teriam ido e vindo sem deixar descendentes diretos capazes de ressuscitar o processo. A vida como a conhecemos consiste tanto de química e informações. Se a vida metabólica já existiu na Terra primitiva, para convertê-la para a vida como a conhecemos teria exigido o surgimento de algum tipo de sistema de informação em condições que são favoráveis para a sobrevivência e manutenção de moléculas informativas genéticas. (Ribas de Poupkna, Ph.D.)
Os agentes inteligentes têm freqüentemente objetivos finais em mente, e usam altos níveis de informação complexa instrucional para cumprir a meta. Em nossa experiência, os sistemas de armazenamento de grandes quantidades de informação complexa especificada / instrucional através de códigos e linguagens -, invariavelmente, são originários de uma fonte inteligente. Da mesma forma, os circuitos ou redes de interação coordenada, como por exemplo de dispositivos eletrônicos analógicos sempre podem ser rastreados até um agente causal inteligente. A operação dos dispositivos electrônicos analógicos mapeia muito estreitamente com o fluxo de informação em reações químicas de vias metabólicas (McAdams e Shapiro, 1995). Um mecanismo proposto para tornar as redes metabólicas deve ser capaz de construir de novo, não apenas modificando, um conjunto mínimo de 50 enzimas e complexos circuitos metabólicos integrados com o objetivo final de criar vida. Uma rede metabólica que não está totalmente operacional, não permitirá a vida. Sabemos da nossa experiência que a inteligência é capaz de construir placas de circuitos eletrônicos, e é a única causa conhecida de máquinas irredutivelmente complexas. Como a evolução depende de circuitos metabólicos totalmente instalados, é excluída como possível mecanismo. Há apenas duas alternativas, o acaso / sorte ou necessidade física, que nunca foram observados de ser capaz de construir placas de circuito de configuração e sistemas complexos irredutíveis. A origem da rede de base metabólica das primeiras células é, portanto, melhor explicada através da ação de um agente inteligente.

http://elohim.heavenforum.org/t256-o-argumento-de-um-designer-inteligente-necessario-para-configurar-as-redes-metabolicas-para-a-origem-da-vida
Observação: A existência de vias metabólicas é crucial para a função molecular e celular. Apesar do fato que genomas bacterianos diferem substancialmente em seus tamanhos e repertórios de genes, não importa quão pequenos, devem conter todas as informações para permitir que a célula possa executar muitas funções essenciais que dão a célula a capacidade de manter a homeostase metabólica, reproduzir e evoluir , as três principais propriedades de células vivas. (Gil et al. 2004) De fato, o metabolismo é um dos processos celulares mais conservadas. Ao integrar dados de genômica comparativa e estudos de eliminação de grande escala, o estudo científico de "análises estruturais de um metabolismo mínimo hipotético" propõe um conjunto de genes mínimo compreendendo 206 genes codificadores de proteínas de uma célula mínima hipotética. O documento lista 50 enzimas / proteínas necessárias para criar uma rede metabólica implementada por um genoma mínimo hipotético para a célula mínima hipotética. Os 50 enzimas / proteínas, e da rede metabólica, devem ser totalmente implementados para permitir uma célula para manter suas funções básicas.
Hipótese (Previsão): A origem de vias metabólicas irredutíveis biológicos que também necessitam de regulamentação e e que são estruturadas como uma cascata,
semelhante a placas de circuitos electrónicos, são melhor explicadas pela ação criadora de um agente inteligente.
Experiência: investigações experimentais de redes metabólicas indicam que elas estão cheias de nós com enzimas / proteínas, que requerem para a sua informação de síntese códigos ricos baseados na linguagem, armazenados em DNA. As estruturas hierárquicas têm provado ser mais adequadas para capturar a maior parte das características das redes metabólicas (Ravasz et ai, 2002). Verificou-se que os metabolitos só podem ser sintetizados, se carbono, nitrogênio, fósforo e enxofre e os blocos de construção básicos gerados a partir deles no metabolismo central são disponíveis. Isto implica que as redes reguladoras engrenagem atividades metabólicas para a disponibilidade desses recursos básicos. Então, um circuito metabólico depende do produto de outros produtos, proveniente de outras vias metabólicas, centrais, dependendo um do outro, como em um Cascata. Mais notável é que loops de feedback foram encontrados serem necessários para regular o fluxo metabólico, e as atividades de muitas ou de todas as enzimas em uma via. Em muitos casos, as vias metabólicas são altamente ramificadas, em cujo caso é muitas vezes necessário fazer modificações de fluxos através de parte da rede, enquanto deixando-os inalterados ou reduzi-los em outras partes da rede (Curien et al., 2009). Estes são interligados de uma forma funcional, resultando em uma célula viva. As redes metabólicas biológicas são perfeitamente integradas, de modo que as alterações significativas inevitavelmente danificam ou destroem a função. Mudanças no fluxo muitas vezes exigem mudanças nas atividades de várias enzimas em uma sequência metabólica. Síntese de um metabolito tipicamente requer a operação de muitos caminhos.
Conclusão: Independentemente da sua complexidade inicial, a vida metabólica com base química de auto-sustentação não poderia ter surgida na ausência de um mecanismo de replicação genético assegurando a manutenção, estabilidade e diversificação dos seus componentes. Na ausência de quaisquer mecanismos hereditários, as cadeias de reação autotrófitos teriam ido e vindo sem deixar descendentes diretos capazes de ressuscitar o processo. A vida como a conhecemos consiste tanto de química e informações. Se a vida metabólica já existiu na Terra primitiva, para convertê-la para a vida como a conhecemos teria exigido o surgimento de algum tipo de sistema de informação em condições que são favoráveis para a sobrevivência e manutenção de moléculas informativas genéticas. (Ribas de Poupkna, Ph.D.)
Os agentes inteligentes têm freqüentemente objetivos finais em mente, e usam altos níveis de informação complexa instrucional para cumprir a meta. Em nossa experiência, os sistemas de armazenamento de grandes quantidades de informação complexa especificada / instrucional através de códigos e linguagens -, invariavelmente, são originários de uma fonte inteligente. Da mesma forma, os circuitos ou redes de interação coordenada, como por exemplo de dispositivos eletrônicos analógicos sempre podem ser rastreados até um agente causal inteligente. A operação dos dispositivos electrônicos analógicos mapeia muito estreitamente com o fluxo de informação em reações químicas de vias metabólicas (McAdams e Shapiro, 1995). Um mecanismo proposto para tornar as redes metabólicas deve ser capaz de construir de novo, não apenas modificando, um conjunto mínimo de 50 enzimas e complexos circuitos metabólicos integrados com o objetivo final de criar vida. Uma rede metabólica que não está totalmente operacional, não permitirá a vida. Sabemos da nossa experiência que a inteligência é capaz de construir placas de circuitos eletrônicos, e é a única causa conhecida de máquinas irredutivelmente complexas. Como a evolução depende de circuitos metabólicos totalmente instalados, é excluída como possível mecanismo. Há apenas duas alternativas, o acaso / sorte ou necessidade física, que nunca foram observados de ser capaz de construir placas de circuito de configuração e sistemas complexos irredutíveis. A origem da rede de base metabólica das primeiras células é, portanto, melhor explicada através da ação de um agente inteligente.









Última edição por Admin em Dom Nov 06, 2016 8:55 am, editado 3 vez(es)

